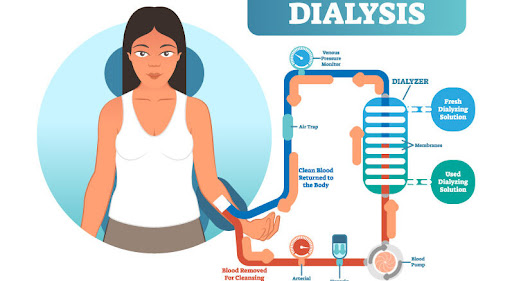
Dialysis is performed in patients with kidney failure, which is the end-stage of chronic kidney failure. That occurs when the kidneys can no longer perform their excretory function and only function between 10 and 15%. It is a therapy “on hold” until a kidney transplant can perform or, sometimes, the only support measure in cases where the transplant is not viable. Today, we will talk about what dialysis is and how does it work.
Some kidney diseases that may require dialysis are uremic encephalopathy, pericarditis, acidosis, kidney failure, pulmonary edema, or hyperkalemia.
What is dialysis, and how does it work?
Dialysis is an alternative blood cleansing procedure. It can excrete contaminants and harmful substances in the blood and excess water in the form of urine. In a healthy person, the kidneys do these things independently. But when the kidneys are crippled, or the ability to purify the blood is lost, or the capacity is reduced, dialysis has to be done to purify the blood. Many people think that only those with long-term kidney disease need dialysis, but suddenly anyone can need dialysis if they have acute kidney failure.
The kidneys maintain the balance of minerals and water in the body of a healthy person. It also produces the essential erythropoietin and cholesterol hormones for blood cell formation. Dialysis cleanses the blood but does not produce hormones.
How does dialysis work?
Dialysis is a procedure that allows replacing the function of the kidneys, at least in part. It is not a curative method but a substitute.
Remember that the kidneys are responsible for removing excess fluids and waste from the blood. All of these wastes leave the body through urine.
When the kidneys are not working properly, these wastes, which are toxins, can build up in the blood. That causes various health problems that, in a short time, can evolve and generate risks to life.
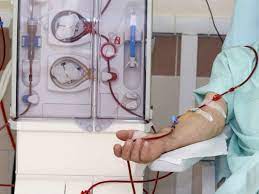
If the kidneys do not perform their work normally, that there is kidney failure. That is when dialysis becomes necessary.
Dialysis fulfills the role of filtering the blood when the kidneys cannot. This procedure should do until those organs heal or a transplant.
However, because you can’t cure kidneys disease always, and not everyone can receive a transplant, some patients must be on dialysis for life.
Types of dialysis and how does it work?
There are two main types of dialysis. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. What type of dialysis will be applicable depending on the patient? Usually, one type of dialysis does not perform on all patients.
Hemodialysis
It will do by machine. In this case, the patient’s blood flows through a machine placed outside the body. The machine only removes waste products from the blood. The blood from the vein goes to the machine through the catheter, is purified, and comes back to the body through another catheter. Hemodialysis usually does three to four hours a week. How much time to do each session depends on the condition of the patient’s kidneys. In some cases, you can do hemodialysis of the patient at home. For example, a healthy patient or whose condition does not change during dialysis, when the patient does not have any other illness.
Peritoneal Dialysis
Sterile dialysis solution, which contains many minerals and glucose. That injects into the peritoneal or stomach through a tube. After that dialysis is complete there the mucous membrane inside the stomach acts like a filter here. If the solution keeps inside the stomach for some time, it will absorb the contaminants from the blood in osmosis. Unlike hemodialysis, it can do for a long time even if it is not effective immediately. The patient can even do it on his own at home. However, it doesn’t take machinery to do it. The patient can do it even if he goes somewhere. It also costs less.
Peritoneal dialysis is again of two types. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis or CAPD. Continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis or CCPD. The first is to do it several times a day. Very simple. The patient or the person with the patient can do it. No machinery requires. The second usually do when the patient is asleep. Usually done every night. It takes 10 to 12 hours. It takes the help of a small machine to do this.
Why is dialysis necessary?
Every day, two kidneys of a healthy person purify one and a half thousand liters (the total amount of blood is so much because the blood goes through the kidneys repeatedly for 24 hours). If the kidneys did not remove waste products from the blood, people would not survive. Also, if one’s kidneys fail to purify the blood or do enough, harmful wastes accumulate in the blood. If the amount of these substances increase, the patient gradually goes into a coma. Even dies. Therefore, dialysis is often necessary in case of kidney damage or kidney disease.
When to start dialysis?
The start of dialysis is usually indicated when kidney failure reaches an advanced stage. The nephrologist analyzes and weights different variables and thus determines if a patient should resort to this procedure.
On the one hand, symptoms take into account and laboratory results on the other. If they indicate that there are significant risks, it will start these types of treatments.
Some of the clinical symptoms that suggest the need to start dialysis treatment are:
- Skin problems
- Lack of appetite, weight loss, malnutrition.
- Digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, and heartburn.
- Fatigue, muscle weakness, and fractures with great ease.
- Difficult-to-control hypertension, heart problems, or feeling short of breath.
- Clotting problems, tendency to have bleeding or anemia.
- Tingling, spasms, tremors, decreased consciousness, drowsiness, or insomnia.
- The usual thing, in any case, is that dialysis is ordered when kidney function is between 8-12%. If these indices drop, the situation can become dangerous for health.
Sometimes a waiting margin is given due to the psychological situation of the patient or other health processes. However, if the clinical situation shows risks, do not wait.
Dialysis is not a substitute for a kidney.
Dialysis can remove some contaminants from the blood, but it cannot do other kidney functions. Patients on dialysis should be careful in drinking water and fluids. You can eat not all types of food. Some medicines also have to be taken. However, patients on dialysis can do other normal things. Women are usually advised not to conceive. However, if you get pregnant in this condition, you have to keep the blood free from contaminants by dialysis.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure
Usually, the kidneys do not fail suddenly is slowly over time. Even if one kidney is OK or both the kidneys are OK or not, there are no symptoms. Usually, when more than half of the kidneys are damaged, some symptoms of kidney failure are seen. Again, not everyone has the same symptoms. The following symptoms may occur.
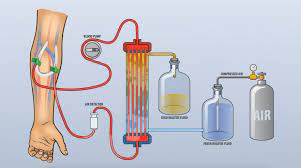
Feeling weak even if you don’t feel extra weakness or work. Frequent urination, especially at night. As time goes on, the speed of urination becomes more frequent.
- Itching of the skin.
- Feeling sick and nauseous.
- Having difficulty breathing.
- Problems with erectile dysfunction.
- Accumulation of water in the hands, feet, and abdomen.
- Blood and protein in the urine.
In some cases, kidney failure can occur suddenly. That is usually due to injury.
Many people with kidney failure also have anemia because the kidneys cannot secrete erythropoietin. Then blood cells are prevented from forming.
What are the causes of complete kidney damage?
Infections, HIV, Hepatitis, Nephritis, Chronic Infections, Polycystic Kidney, High Blood Pressure, Uncontrolled Diabetes, TB, Tuberculosis in Food and Fruits, Radioactivity, Pesticides in Vegetables, etc. In addition, from birth to old age, kidney, ureter, bladder, prostate urethral stones, tumors, or obstruction of urinary excretion, the kidneys become swollen, and gradually the kidneys lose their function. Uterine or ovarian tumors often cause kidney failure in girls. Again, a large tumor in the esophagus or stomach obstructs the kidneys and ureters, but the kidneys are damaged. Many times, the kidneys will also damage by taking extra pain pills.
Side Effects and Risks of Dialysis
As with most medical procedures, dialysis can also cause side effects. The usual thing is that cramps, itching, and low blood pressure are present. It is common.
In the long term, more serious problems such as amyloidosis or abnormal storage of amyloid material can occur. Cardiovascular disease, dementia, autonomic neuropathy, and blood loss leading to iron deficiency can also occur.
Hygienic conditions are very important since one of the risks is that of contracting an infection. On the other hand, some patients have reported difficulties sleeping after dialysis or sleep apnea. It is also relatively common for the procedure to induce weight gain.
FAQ on What is dialysis and how does it work
What is the type of dialysis utilization in hemodialysis?
The dialogues to supplement the defiance of the sick in assuring the elimination of dachshunds and the organization. On distinguishing globally, there are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and hemodialysis, external to the font.
How to take care during dialysis?
Lie and gaze at the television during the dialogue
“Patients support their laptops,” added Gino Matthys. In certain dialysis centers, it is possible to surf the internet. If you use the perimeter, making the telepathic the hospital is not even possible.
How does the dialysis function work?
Peritoneal Dialysis (DP) is a substitution method for the terminal suffocation of personal terminals. It allows purifying the blood by using the peritoneum, membrane surrounding the abdomen, the intestine, and other internal organs as a filter.
What are the dangers associated with dialysis?
Risks Frequencies (between 1 and 10%)
Hypotension Artifacts, malaise, cramps, nausea, vomiting, irregularities in baths, humor or hemorrhoids, or nausea at the point of sleep or oversleep. Fatigue approaches dialysis.
Conclusion on What is dialysis and how does it work.
Many people believe that the patient can no longer be saved once dialysis is done or does not survive, but regular dialysis keeps the patient healthy. However, those who do irregular dialysis may experience a variety of physical complications. Such as loss of appetite, anemia, shortness of breath, swelling of the body, etc., may occur.